Helminthiasis is a parasitic disease that is particularly common in children. If worms appeared in any of the organs or systems of the child's body, their negative impact will not only affect its functioning, but also affect the work of the immune and nervous systems. Symptoms such as cough, lack of appetite, indigestion, allergic reaction may be accompanied by other unrelated symptoms. If you suspect a helminthic invasion, it is important to immediately contact a specialist and not self-medicate.

Why are helminthiasis dangerous?
Most helminth infections of the species most commonly found in children parasitize the intestines. They live and feed there, allowing them to reproduce and release toxins. Parasitic worms also mechanically affect the walls of the intestine. The consequence of the active life of worms in the body of a child can be:
- Avitaminosis and weight loss. These problems arise due to a lack of nutrients and vitamins. As a result, children begin to lag behind in their development. Pathological processes can begin in other organs.
- Inflammation in the intestines, colitis, dysbacteriosis, bleeding. All these unpleasant and serious complications are caused by mechanical damage caused by worms in children in the body.
- The development of inflammatory processes in the appendix, liver, gallbladder. These are organs adjacent to the intestines through which parasites can travel.
- Intestinal obstruction. It can be partial or complete, and there is sometimes a risk of rupture of the intestinal wall.
- body poisoning. When worms live and die inside a person, they release aggressive toxins.
- Allergy. Parasite waste products are considered strong allergens.
- Violation of the functioning of the liver. For this reason, the child must follow a diet for many years and additionally consume enzymes.
- Psychosis. Helminths tend to have a negative impact on the patient's nervous system.
Types of worms that affect a child's body
There are many types of parasites that can appear in a child's body. They vary in size, being both small and large, and also manifest in different ways and have a different incubation period, which varies from 1 to 1. 5 months. In order to prescribe effective drugs that will help cure helminthiasis, you need to correctly determine their type. The most common types in children are:
- Ribbon. This type of worm includes cestodes, pygmy tapeworm, tapeworm, and echinococcus.
- Surrounded. Among them are the annelids.
- Round. Their representatives are trichinella, pinworms, whipworms, nematodes, roundworms.
- Spicy head. They are represented by scrapers.
- Apartment. Among them are trematodes and flukes.
Causes and methods of infection
It is possible to become infected with helminthiasis not only in an exotic country or by trying an unusual dish on the menu. Playing in the sandbox and unwashed hands is the easiest way for worms to enter the child's body. Toddlers tend to touch and study everything, without thinking about the purity of the subject being studied. After that, they can safely lick their fingers without washing them first. Worms remain viable for a very long time (from several weeks to several months), remaining on the surface of various objects.
In addition to dirty hands, major sources of infection include:
- dirty toys and surfaces;
- clothes;
- shoes;
- railing at the entrance;
- door handles;
- natural water;
- dirty vegetables and fruits;
- ground, earth, sand;
- contact with a sick child;
- undercooked meat;
- improperly heat-treated fish or other seafood.

Symptoms of Parasites in Children
Usually, in children under 1 year old, any manifestations of the presence of parasites in the body are observed in isolated cases. The first symptoms that signal an infection with helminths are recorded already at an older age (about 2-3 years) in children attending a kindergarten or other developing organizations.
Helminthiasis in children is represented by a wide variety, and each individual type has its own specific characteristics. However, there are a number of characteristic symptoms of any type of worm:
- irritability and mood swings for no apparent reason;
- agitated sleep;
- allergy;
- itching in the anus;
- increased saliva secretion;
- disturbed digestion, accompanied by diarrhea, constipation, nausea and bloating;
- lack of appetite;
- weight loss with proper nutrition;
- pallor of the skin.

In adult children, these symptoms may include:
- headache;
- discomfort in the stomach;
- dizziness;
- increased fatigue;
- poor focus.
Enterobiasis (pinworms)
A disease when parasites such as pinworms enter the child's body is called enterobiasis. This type of helminths is one of the most common in young children of preschool age - from 2 to 5 years old. They differ in average sizes, which are from 5 to 13 mm, and minimal damage compared to other types of pests.
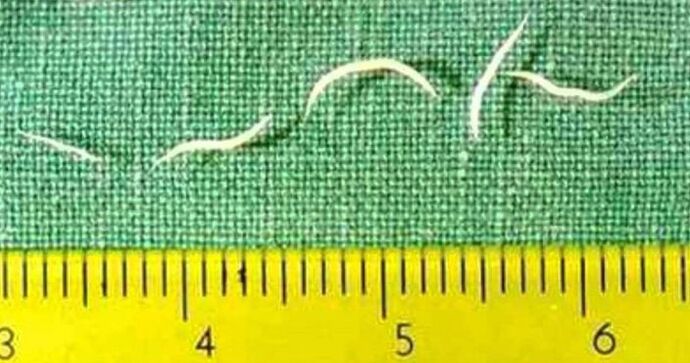
Their presence causes the appearance of the following symptoms:
- Violent itching in the anus. Its intensity can reach such a strength that the child will not sleep well, scratching the anus, causing irritation and inflammation.
- Urinary incontinence during nocturnal sleep. Seen in girls. This happens if pinworms from the anus enter the urethra. As a result, the baby begins to develop urethritis, vaginitis or cystitis.
Pinworms are easy to remove and are not as dangerous as other types of worms. It is important in time, when the first signs appear, to consult a doctor and take the necessary tests. If pinworms were found in a child, parents also need treatment. All clothes, towels and other rags should be washed and ironed, and the room thoroughly washed, as the eggs of these worms are found on all surfaces of the infected person's home.
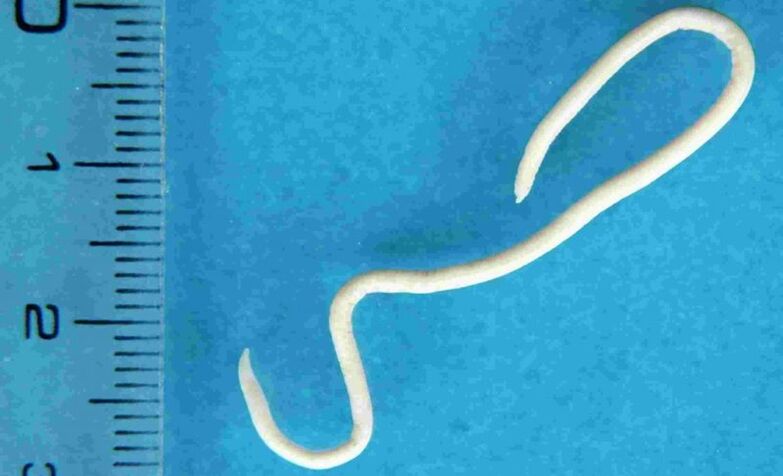
Ascariasis (roundworm)
The most common roundworms in children are large roundworms up to 40 cm, living in the small intestine - roundworms. In addition to the general symptoms of helminthiasis, in the case of ascaris, a person infected at the initial stage develops an unreasonable cough in the absence of any inflammatory processes in the respiratory tract. Its appearance is due to the fact that the larvae of this type of parasites enter the lungs and upper respiratory tract and, through coughing, enter the stomach.
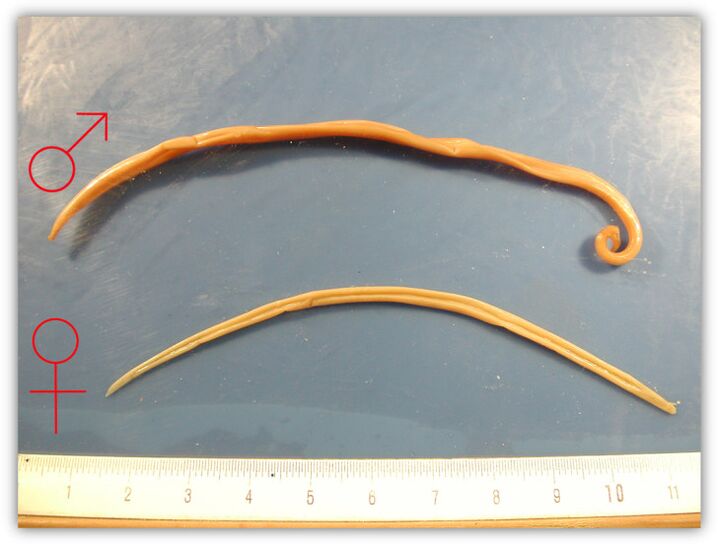

Other features include:
- headaches and dizziness;
- allergy;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- high temperature;
- intestinal disorders.
At the same time, itching in the buttocks with roundworms is absent. Not only the intestines, but also any other organ or body system can become a habitat.
Trichuriosis (moustachioed)
These parasites in children are worms with a very thin body, the length of which reaches 5 cm. The female whipworm can lay up to 2, 000 eggs at a time. Usually these helminths are more common in adolescence, and in young children they appear much less frequently.
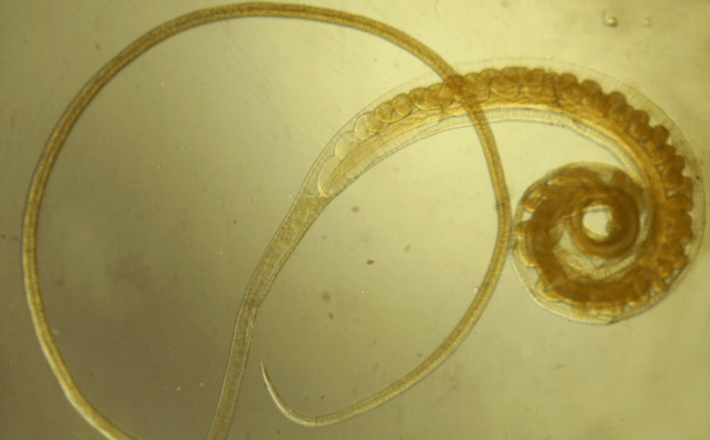
A distinctive feature of trichocephalosis is the almost complete absence of any signs of helminthic invasion. Possible symptoms include:
- disturbances in the work of the nervous system (irritability, headaches);
- problems with the digestive system, accompanied by diarrhea, nausea or vomiting;
- increase in body temperature.
Signs of other parasites
Other types of worms that can occur in children include:
- Hymenolepiasis or tapeworm in the pygmy rat. He has no particular symptoms. Its presence can be recognized by nausea, loss of appetite, heartburn, diarrhea and constipation, headache, abdominal pain, increased salivation, dizziness, fatigue, rashes, allergic rhinitis and bronchospasm.
- Opisthorchiasis or Siberian fluke in cats. These worms in a child cause subfebrile temperature, rashes, swollen lymph nodes, pain in the joints and right hypochondrium, pancreatitis, gastritis and other signs of dysfunction of the digestive tract, permanent catarrhal syndrome, etc.
- Toxocariasis. Transmitted by animals. The main symptoms are an allergic cough with choking and rashes, characterized by severe itching.
- Wide ribbon. The source of infection is not fried or boiled fish. Symptoms include abdominal pain, allergic reaction, vitamin B12 deficiency anemia, and other common signs of a bowel disorder.
How to check if your child has worms?
In most cases, it is difficult for parents to associate specific symptoms with helminthiasis or to understand why a child suddenly has vomiting or other symptoms for no apparent reason. At the slightest suspicion of the appearance of worms, it is necessary to turn to specialists and take tests, which make it possible to easily verify the hypothesis of helminthic invasion. It will not take much time and effort, but the reason for the baby's illness will be completely clear, and it will be possible to carry out timely treatment.
Self-diagnosis
Self-diagnosis is careful monitoring of changes in the behavior, development, habits, routine and normal state of the child - both physical and emotional-psychological.
He understands:
- periodic examination of feces for the presence of worms;
- monitor the frequency of bathroom visits;
- examine the skin for rashes, redness or irritation;
- check the amount of food eaten.
Test
Medical diagnosis is needed to confirm the diagnosis if worms were detected visually, or only if helminthic invasion is suspected. To determine the cause of the symptoms, you must undergo a series of tests, including:
- Fecal analysis. You will find eggs or parts of already mature worms there. The effectiveness of the method is greatest during the period when there are already mature individuals in the intestine, that is, about 3 weeks to a month after infection. Feces should be collected in the morning and sent to the laboratory.
- A smear or scraping from the anus. To do this, use a dry cotton swab moistened with glycerin or adhesive tape. The analysis allows you to identify the larvae of worms that have settled on the skin areas of the anus.
- General blood test. Patients with helminthiasis in the blood may have an increased number of immune cells, a high sedimentation rate of erythrocytes and a reduced level of hemoglobin.
- ELISA blood test. Detects parasites at an early stage using staining enzymes that attract worms, viruses and other foreign bodies.
Additional tests for parasites in a child that can be done on an outpatient basis include:
- analysis for the presence of IgG antibodies;
- ultrasound procedure;
- x-ray.
Features of drug therapy
The appointment of drugs to combat parasites in a child should be taken up by a doctor after passing all the required tests and establishing an accurate diagnosis and the type of worms. Among the most common drugs for helminthic invasion, it should be noted:
- Anthelmintic drug acting on nematodes. Acceptance is permitted from 6 months. Effective against all types of roundworms, but useless against flat parasites.
- Anthelmintic drug from the benzimidazole group. Appointed from 2-3 years. The dosage is determined at the rate of 10 mg per kilogram of body weight.
- Antiprotozoal and antimicrobial drug from the group of nitroimidazoles. Suitable for any age, depending on which the daily dose is determined.
- An anthelmintic drug from the group of benzimidazoles. For children from 2 years against roundworms.
What folk remedies can help?
In addition to medication, worms can be treated with folk remedies.
The most popular products that can provide effective treatment for worms in children are:
- Garlic. Successfully destroys roundworms, tapeworms, pinworms and copes with many other varieties of pests. Suitable for children from 5 years old with a healthy stomach. It should be given 1 clove before meals once a day. Can be taken with water or milk. Garlic is also an excellent antiviral agent.
- Pumpkin seeds. They should be eaten on an empty stomach and raw. Usually children like this treatment. Alternatively, they can be crushed and mixed with honey if the child is not allergic to honey.
- Mugwort. Authorized for children from 12 years old. To simplify the reception, it should be mixed with a piece of bread and salt.
- Fresh carrot juice. Enough half a cup on an empty stomach once a day for 7-10 days. You can also snack on raw carrots.
- Beet juice. It is administered on an empty stomach. It is advisable to alternate it with carrots, so as not to cause a violation of the stool.
- Nut. A few pieces a day will be enough for a child.
- A pineapple. Fresh, not canned fruit is a tasty and effective remedy.
- citrus. To their "company" you can add sour-tasting berries and fruits.
Prevention
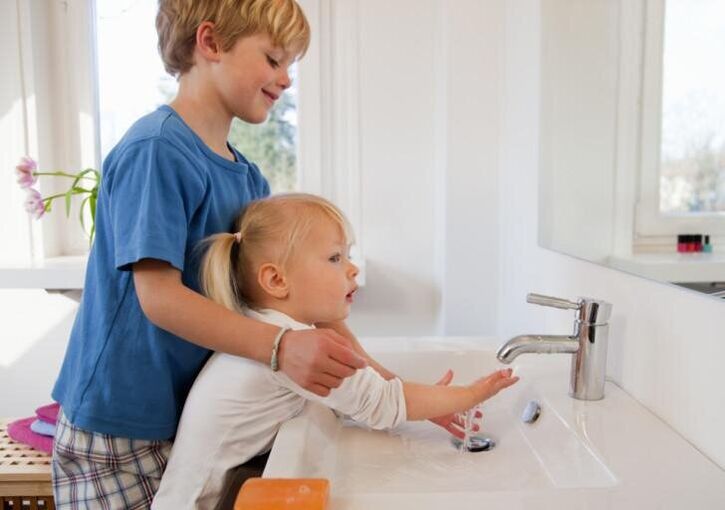

Whatever the type of worm, prevention comes down to respecting the basic rules of personal hygiene:
- Washed food. All vegetables, fruits and berries should be washed well before eating. As an additional measure, the products can be doused with boiling water.
- Clean hands. You should wash them before eating, after walking, visiting the hospital and staying in public places, after going to the toilet and playing with animals, even pets.
- Deworming pets. It should be done at least twice a year.
- Boiled or filtered water for drinking. It is forbidden to drink water from open reservoirs. It is also necessary to avoid bathing in it to prevent splashes of water from entering the mouth. Exceptions are salt lakes and seas.
- Regular prevention with the help of folk remedies.
- Take care of old and new toys. Soft toys should be washed periodically, plastic and plastic ones should be washed in boiled water. New ones, before giving them to a child, must be poured with boiling water without fail.
- No insects! Flies, mosquitoes, cockroaches carry helminth eggs on their paws. It is important to prevent them from entering the house. To do this, you can use fumigators, tapes and special pencils.
- Exclusion from the child's diet of fish and meat dishes that require low roasting of animal products.
- Stool analysis once a year. This procedure will help detect worms at an early stage.